
-
Will self-driving ‘robot labs’ replace biologists?February 2026
Meagan Olsen and Professor Jewett weigh in on the role of AI-driven autonomous robots in synthetic biology research.
Read the opinion piece here!

-
Michael C. Jewett is elected to the American Academy of MicrobiologyFebruary 2026
Fellows of the Academy are elected annually through a highly selective, peer-review process based on their records of scientific achievement and original contributions that have advanced microbiology. Congrats, Mike!
See the full list of 2026 Academy Fellows here!

-
Jewett Lab ‘ReForm’s the world one molecule at a timeFebruary 2026
The Stanford Daily covers the Jewett Lab’s most recent pubclished work, ReForm, a platform aiming to curb the effects of climate change by transforming wasteful carbon into acetyl-CoA.
Check out the article here!
-
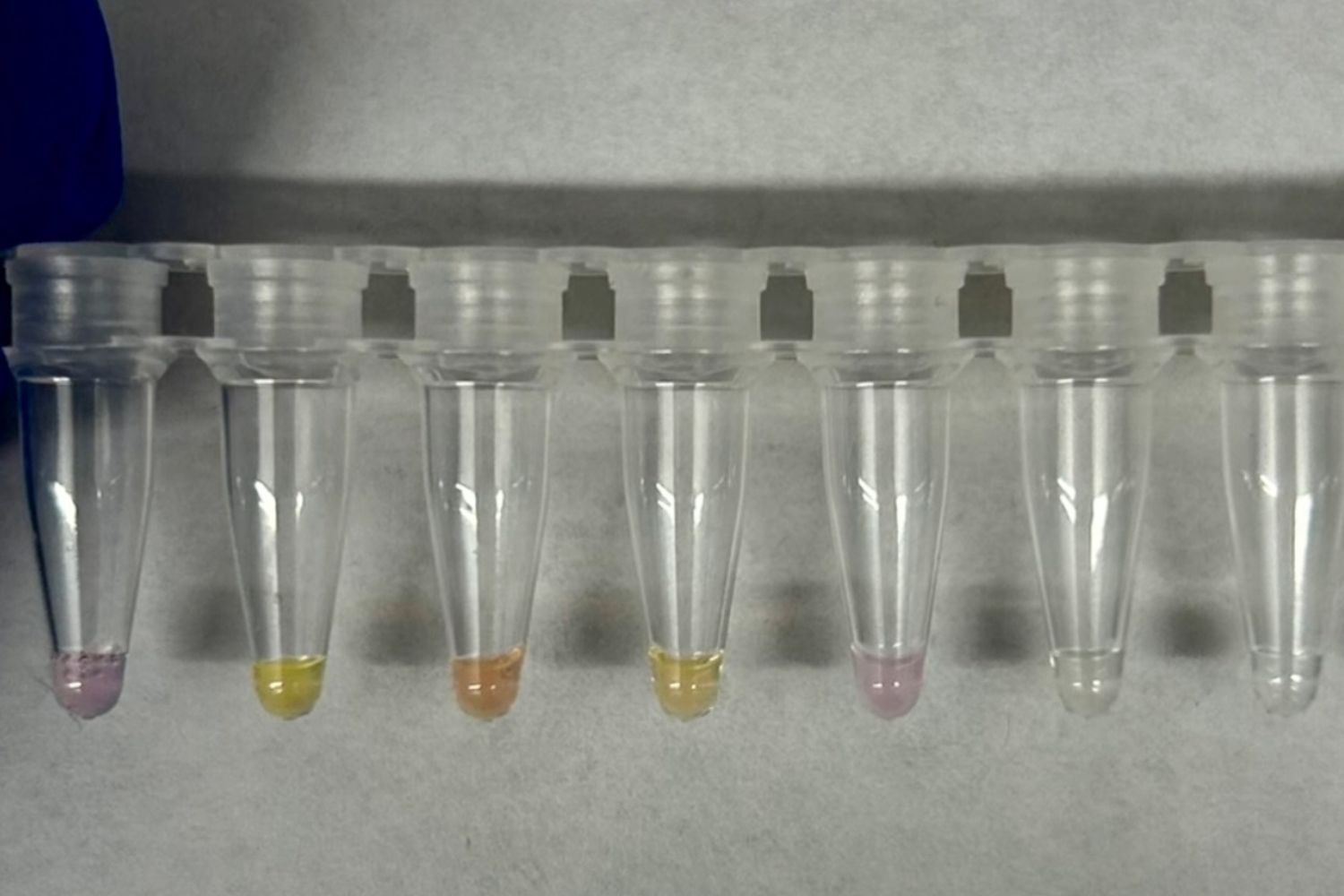
A groundbreaking new system paves the way for advances in synthetic biology and carbon recyclingJanuary 2026
The Jewett Lab has engineered a biological system that can convert formate – a simple liquid molecule easily made from CO2 in the atmosphere – into acetyl-CoA, a universal metabolite used by all living cells. The work could lead to the development of sustainable, carbon-neutral fuels and materials.
Read more about the study in the Stanford Report here!

-
Synthetic biologists have created a new artificial metabolism that transforms waste carbon dioxide into useful biological building blocksDecember 2025
This breakthrough enables new, scalable approaches to carbon-negative manufacturing, opening pathways to sustainable fuels, materials, and chemicals that recycle CO₂ rather than emit it.
Read more about the workhere!

-
New Jewett Lab publication is featured in the Dutch daily newspaper, De VolkskrantDecember 2025
American researchers have succeeded in converting CO2 into malic acid, a substance found in apples, candy, and wine, among other things. The research results were published this week in the journal Nature Chemical Engineering.
Check out the article here!

-
Stanford hosts the inaugural Stanford Synthetic Biology ExpoSeptember 2025
The Expo featured talks and posters from multiple departments here at Stanford. Special thanks to Anru Tian, Mike, and the rest of the planning committee for making this possible!
Read more about the expo here!

-
Northwestern University hosts the 3rd international Cell-free Systems ConferenceSeptember 2025
The Center for Synthetic Biology hosted the 2-day event where leaders of the field gathered to discuss the promises and challenges of cell-free systems.
Read more about the conference here!

-
Michael C. Jewett Is AIChE’s 2025 Acrivos Professional Progress Award RecipientSeptember 2025
The Andreas Acrivos Award for Professional Progress in Chemical Engineering is endowed by the AIChE Foundation and recognizes outstanding progress in chemical engineering by a member of AIChE in their early career.
Read more about Mike and the award here!

-
NSF invests $32M to accelerate novel AI-driven approaches in protein designAugust 2025
This inaugural investment supports 5 projects including the Jewett Lab’s new collaborative work with Novozymes Inc. to produce complex human milk oligosaccharides.
Read more about the investment and other funded projects here!

-
Michael C. Jewett shares how Stanford researchers are producing greener chemicals, more climate-resilient agriculture, and new ways to repurpose food wasteApril 2025
In this Q&A, Jewett explains a bit of background about this field and exciting projects already in the works to enable new solutions for planetary health.
Read more about it here!

-
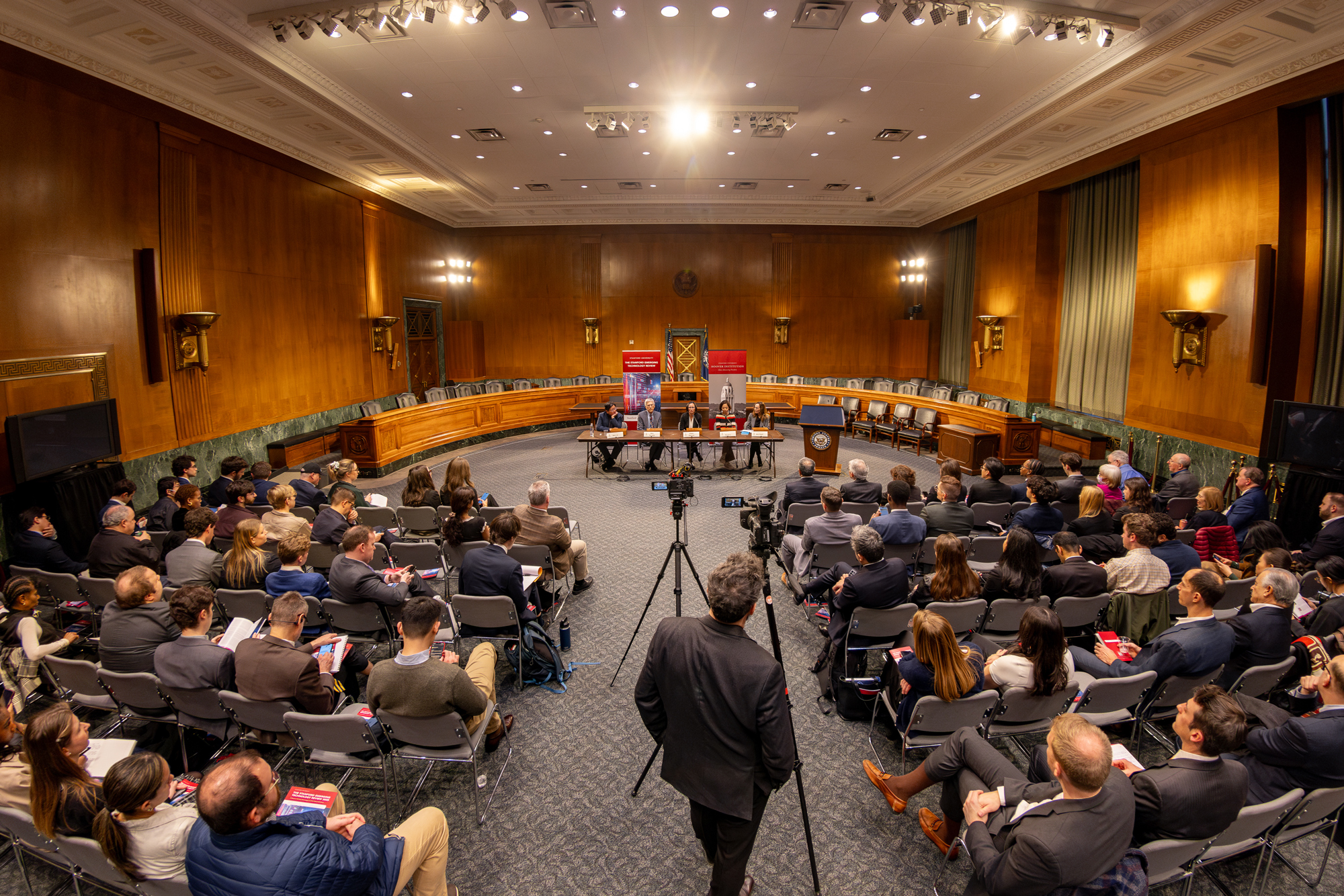
The release of the 2025 Stanford Emerging Technology Review (SETR) highlights the importance of synthetic biology and biotechnology.March 2025
The report—produced through the SETR initiative, based on leading research from Stanford scientists, engineers, and policy experts—serves as a primer into state-of-the-art innovations in ten key domains and what to look out for in the future. The goal of the partnership is ambitious: to transform technological education for decision makers in both the public and private sectors so that the US can seize opportunities, mitigate risks, and ensure that the American innovation ecosystem continues to thrive.
Read the highlights here!
Read the Stanford Emerging Technology Review 2025 here!
-
‘Democratizing biology’: Stanford bioengineering lab provides affordable gene-editing kit for high school studentsFebruary 2025
CRISPRKit allows students to analyze gene-editing outside of a lab setting with only a smartphone. It marks one step forward in the bigger movement to make complex scientific innovations, such as gene-editing, more understandable and accessible for today’s youth.
Read more about it here!
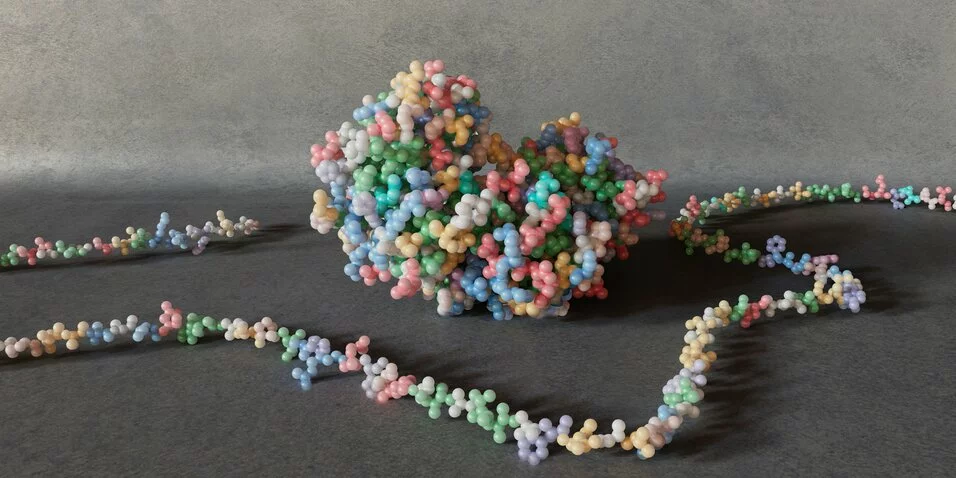
-
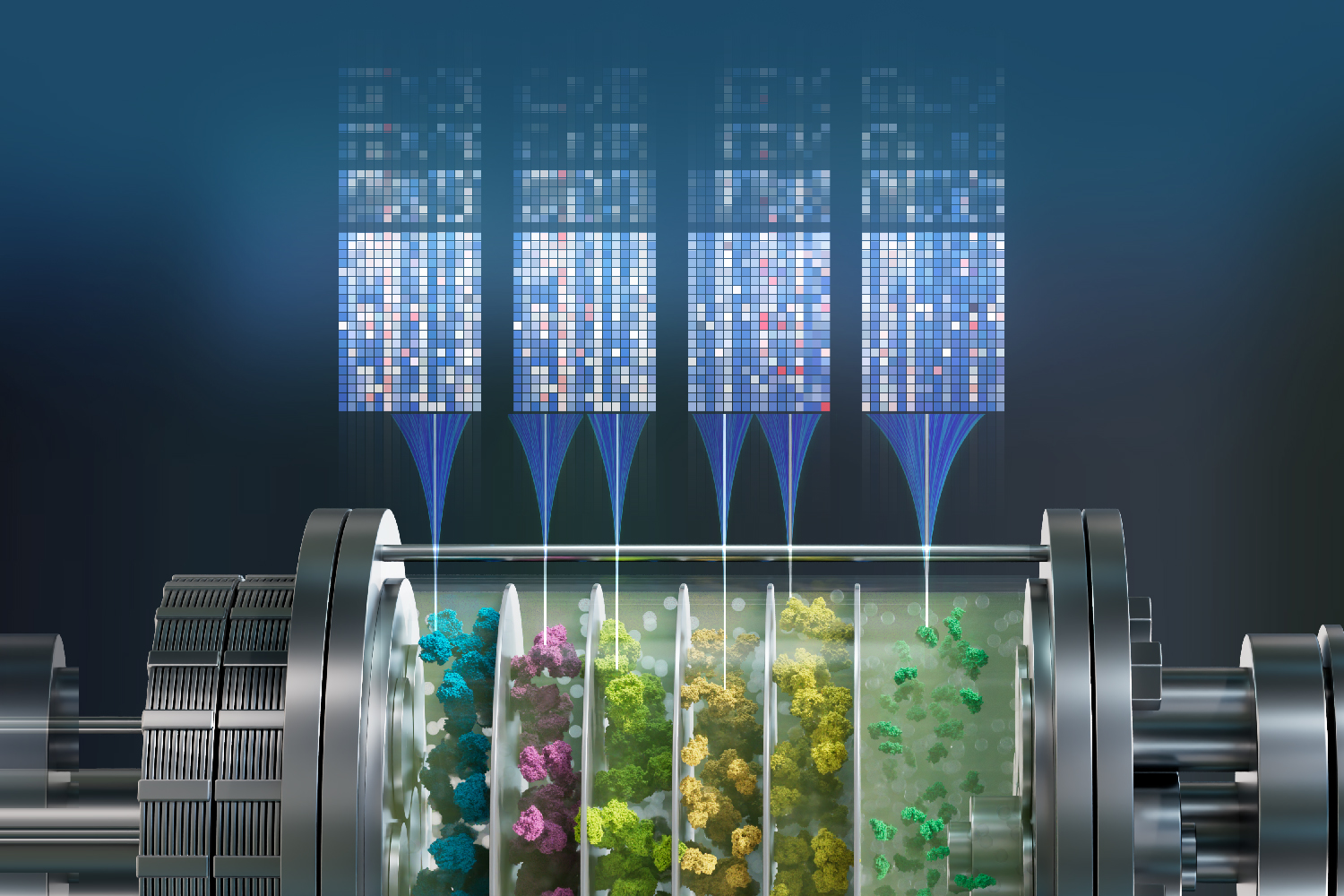
AI Accelerates Enzyme EngineeringJanuary 2025
“We’ve developed a computational process that allows us to engineer enzymes much faster because we don’t have to use living cells to produce the enzymes, as is now the case. Instead, we use machine learning to predict highly active designer enzymes that have been engineered from mutated DNA sequences modeled on the computer instead of created by hand in the lab. We can carry out these experiments in days rather than weeks or, as is often the case, months.” said Michael Jewett. In this work, the Jewett lab was able to assess 3,000 enzyme mutants across about 1,000 products and about 10,000 chemical reactions.
Read more about it here!
-
In the hunt for new and better enzymes, AI steps to the foreJanuary 2025
Combing through scads of DNA, chemical structure, and functional data, researchers have created an AI-guided platform that helps design, build, and test powerful new enzymes.
Read more about it here!

-
ML-Guided Enzyme Engineering Advances Green ChemistryJanuary 2025
This new high-throughput, cell-free platform could create versatile biocatalysts for sustainable chemistry. “Engineered enzymes are poised to have transformative impacts on the bioeconomy across numerous applications in energy, materials, and medicine,” said corresponding author and Assistant Professor at Northwestern’s Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering Ashty Karim.
Read more about it here!

-
Stemloop Awarded Funding from DARPA’s Artificial Intelligence and Biotechnology Initiative to Enable Machine Learning for BiosensorsDecember 2024
Stemloop’s next-generation biosensor technology can be used to detect contaminants in food and water, accelerate research in the life sciences, and enable next-generation wearables for health and wellness monitoring. “While traditional methods are costly and slow, Stemloop’s biosensors overcome these barriers with rapid, cost-effective, and easy-to-use solutions powered by cell-free synthetic biology,” said Stemloop co-founder Michael C. Jewett, Ph.D.
Read more about it here!

-
ASBMB TODAY article: Nobel for ‘breakthrough in biochemistry’October 2024
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Baker’s group collaborated with scientists including Michael Jewett, to design “miniprotein inhibitors” to block the SARS-CoV-2 virus’ interaction with its receptor. Baker and collaborators created a nasal spray containing that potent novel miniprotein inhibitor, and it is now in clinical trials for protecting against SARS-CoV-2.
“These innovations change the way people think about proteins and how they do protein science,” Jewett said. “Success in harnessing AI and computational predictions of protein structure is bringing new solutions to address some of society’s greatest challenges in human and planet health.”
Read more about it here!

-
Mike is highlighted in Cell Chemical Biology’s 30th Anniversary Special IssueSeptember 2024
Michael C. Jewett: Chemical biology is an interdisciplinary research field where chemical tools and technologies are used to probe, understand, and build with biology. Research efforts span multiple scales, from molecular to cellular, and are applied to natural and new-to-nature systems.
Read more about it here!
-
Kit makes CRISPR education affordable and accessibleSeptember 2024
“Our goal is to democratize biology,” said Lau. “The demand is there – this could serve as a model to bring these kinds of opportunities to classrooms.”
Read more about it here!
-
Science in 60 SecondsJuly 2024
Ravalika Damerla, a BioE PhD student in the Jewett Lab introduces her research on utilizing cell-free systems for fungal enzyme expression.
See more about it here!
-

-
Scientists have created an organism that defies the rules of biology by using nonstandard amino acidsSeptember 2023
“We decided to build the seatbelt before the car,”. The biocontainment strategy relies on a property called “synthetic auxotrophy.”
Read more about it here!
-

-
Chemists convert electricity into the fuel that powers the body’s cellsAugust 2023
“ATP generated with renewable power could potentially be used to manufacture proteins and medicines”
Read more about it here!
-

-
Cell-Free Synthesis of Peptidomimetic Drugs by International Research TeamApril 2023
“Cell-free protein synthesis offers exciting benefits for making peptidomimetic drugs because of the freedom of design to incorporate non-canonical chemistries when working without the constraints of living organisms,” says one of the authors, Michael Jewett, PhD, professor of bioengineering at Stanford University (formerly at Northwestern University). “Put another way, we are able to repurpose the molecular machinery of the cell to make new-to-nature products that have therapeutic benefit.”
Read more about it here!
-

-
How cell-free processes could speed up vaccine developmentMarch 2023
Cell-free vaccines and other cell-free innovations step ever closer to becoming commercially viable, thanks to researchers like Mike Jewett. Biochemical engineering breakthroughs not only promise advances in manufacturing, but storage and transport as well!
Read more about it here!
-

-
Mike Jewett, TEDxChicago: Make anything, anywhere with just-add-water biotechnologyJanuary 2023
Hey party people – the wait is over! Mike’s TED talk with TEDxChicago invites viewers into a world of scientific imagination, led by his vision to re-think how biotechnologies are created and shared, and made possible by biology without cells. Mike poses the questions, can just-add-water biotechnology turn us all into biomakers, and does it make possible on the frontiers of medicine, diagnostics and much more!
Check it out here!
-

-
“Just Add Water” – Low-Cost, Thermostable CFPS Biomanufacturing Platform Obviates Cold ChainJanuary 2023
An inexpensive, thermostable, cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS) platform for decentralized vaccine production has been developed by the Jewett Lab and collaborators. Because glycosylated products now can be produced in a lyophilized CFPS system, “This creates opportunities to target many diseases and manufacture medicines for deployment in resource-limited settings that current economics simply do not allow,” says Jewett, calling this a “just-add-water” CFPS system. “Think of it like baking: we mix wet and dry ingredients along with a recipe encoded in DNA to make vaccines. This opens a lot of exciting opportunities to make medicines by just changing the DNA.”
Read more about this exciting development here!
-

-
Northwestern and MIT receive funding from Army’s synthetic biology centerJanuary 2023
Collaborations between Northwestern and MIT have secured funding from the Army’s synthetic biology center. NU’s project, titled “The Center for Predictive Materials Design (PreMaDe),” is lead by Mike Jewett and hopes to combine synthetic biology and materials expertise with engineering and computational modeling strengths to create new biomaterials with precise control over their functional properties. Potential applications of such materials include electronic circuitry for wearable electronics, optical materials that dynamically sense and respond to their environment, and rugged cell-free materials with embedded sensing and actuation functions for molecular diagnostics.
Read more about it here!
